What are Retained Earnings? Guide, Formula, and Examples

They’re part of shareholders’ equity on the balance sheet and reflect the company’s accumulated profits over time. Consider a homeowner who saves money from their salary to pay down their mortgage or to renovate their house. The decision to use those savings to reduce debt or improve the home (equity) is a financial decision about how assets are funded or allocated. To this beginning balance, the company’s net income (or net loss) for the current period is added.
Are Retained Earnings a Type of Equity?
By recording profits in retained earnings, the company increases its assets and enhances its value without incurring debt. On the balance sheet, retained earnings appear under the “Equity” section. “Retained Earnings” appears as a line item to help you determine your total business equity. You have beginning retained earnings of $4,000 and a net loss of $12,000. When a company reinvests its retained earnings into the business, it typically results in an acquisition or growth of assets, such as machinery, inventory, or property. Companies can manipulate them to some extent through accounting methods, potentially impacting the accuracy of this metric.

What is the Retained Earnings Formula?
![]()
Retained earnings are consistently classified as an equity account on the balance sheet, not an asset. While a company’s profits do increase its assets, such as cash or inventory, the retained earnings account itself is merely a record of where those increased assets originated. They illustrate the source of a company’s financing, representing cumulative profits kept within the business to fund operations or expansion.
- They are distinct from liabilities because they do not represent a debt to be repaid to an outside entity.
- These earnings represent a crucial source of internal financing for business growth, debt reduction, and operational needs.
- Property, plant, and equipment, such as land, buildings, and machinery, are long-term assets used in operations.
- Assets are reported on a company’s balance sheet, typically grouped by their liquidity.
- Or you can use retained earnings to pay off debts and take that stress off your shoulders.
- Negative retained earnings suggest the company has experienced cumulative losses, which can erode shareholder equity and raise concerns about financial viability.
The Relationship between Retained Earnings and Assets

In this case, some people may confuse retained earnings for liabilities. However, this balance does not meet the definition for any of those items. Usually, these include retained earnings asset special dividends that differ from the year-end allotments. Retained earnings is the cumulative amount of earnings since the corporation was formed minus the cumulative amount of dividends that were declared. Retained earnings is the corporation’s past earnings that have not been distributed as dividends to its stockholders.
- Still, it plays a crucial role in defining the company’s ability to strengthen its asset base.
- And while that seems like a lot to have available during your accounting cycles, it’s not.
- Retained earnings represent a crucial element of shareholder equity, reflecting the cumulative net income that a company retains after distributing dividends to shareholders.
- Retained earnings are also crucial when it comes to dividend policy decisions.
- Therefore, it’s essential for investors, creditors, and stakeholders to understand and analyze retained earnings when evaluating a company’s overall performance and financial standing.
- In some cases, the corporation will use the cash from the retained earnings to reduce its liabilities.
Real Life RE/TA Ratio Examples
- You can use this calculator to figure out your retained earnings account’s balance at the end of your accounting period.
- Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income of a company not distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- They show how much profit a business has held onto over its operational life.
- Companies with high retained earnings typically have lower dividend payout ratios, as more profits are retained for reinvestment.
- This placement reinforces that they are a component of equity, illustrating how a company’s assets are financed.
- If a potential investor is looking at your books, they’re most likely interested in your retained earnings.
Overall, retained earnings are a critical factor in financial analysis because they reflect the company’s historical ability to generate profits and manage dividend distributions. Changes in retained earnings can signal shifts in business strategy, profitability, or financial health. Another important ratio is the debt-to-equity ratio, which compares a company’s total liabilities to its stockholders’ equity. Since retained earnings add to equity, an increase in retained earnings can reduce the debt-to-equity ratio, indicating a stronger equity base relative to debt.
Leverage retained earnings for business success
We can find the net income for the period at the end of the company’s income statement (consolidated statements of income). Strong financial and accounting acumen is required when assessing the financial potential of a company. Therefore, it’s essential for investors, creditors, and stakeholders to understand and analyze retained earnings when evaluating a company’s overall performance and financial standing. Retained earnings are not an asset per se but play an important role in the growth and expansion of a company’s assets.
- Understanding retained earnings is essential for financial professionals, investors, and business managers alike in interpreting financial health.
- However, note that the above calculation is indicative of the value created with respect to the use of retained earnings only, and it does not indicate the overall value created by the company.
- In contrast, when a company suffers a net loss or pays dividends, the retained earnings account is debited, reducing the balance.
- Retained earnings are recorded under shareholders’ equity, showing how these earnings can be used as a tool to generate growth.
- Retained earnings are not assets; they are a component of owner’s equity on the balance sheet.
- Retained earnings are a fundamental component of owner’s equity, measuring a company’s accumulated profitability.
(No offense, accountants.)Essentially, it’s the total income left over after you’ve deducted your business expenses from total revenue or sales. You can find it on your income statement, also known as what are retained earnings profit and loss statement. Retained earnings are the total profits a company has earned over time, considering that it didn’t give those profits to its shareholders as dividends. How can you see a snapshot of your business’ financial situation at any time? This special report tells you about the things your business owns and what it owes to others, as well as how much value your business has for its owners.
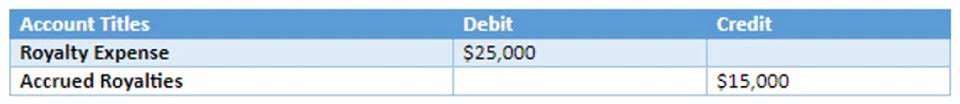
Accumulated Losses and Negative Retained Earnings
Additional paid-in capital does not directly boost retained earnings but can lead to higher RE in the long term. Additional paid-in capital reflects the amount of equity capital that is generated by the sale of shares of stock on the primary market that exceeds its par value. Retained earnings are reported under the shareholder equity section of the balance https://saasipaint.com/2021/07/28/special-journals-financial-accounting/ sheet while the statement of retained earnings outlines the changes in RE during the period.

Deixe uma resposta